DIAMOND EDUCATION
Diamonds were formed deep in the earth more than a billion years ago under high pressure and high temperatures. Diamonds are made up of only one element… carbon, and are 58 times harder than anything else on earth. Diamonds are extremely rare. The average yield of a diamond mine is only one part diamond to every 1,000,000 parts host rock. Diamonds are found in a rough state and then purchased by diamantaires to cut, polish and sell to the open market.
How to Buy a Diamond
your diamond search
If you are just starting your search for a diamond or engagement ring, you should familiarize yourself with the Four C’s which stand for cut, color, clarity and carat. The diamond industry standard is to use the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) grading scale. However, Underwood’s goes one step further and also grades our diamonds to the stricter standards of the American Gem Society (AGS).
GIA and AGS are both non-profit organizations that were founded by the same person, Robert M. Shipley, in 1931 and 1934. AGS has a ten grade cut grading system that goes much further than GIA’s five cut grades, allowing them to be the leaders of cut grading in the World. AGS uses a scale from zero to ten, with zero being the best and ten being the worst. By using ten cut grades instead of five, it allows Underwood’s to find the best cut diamonds for our customers. It’s about beauty and science.


ASET images and how they should and should not look:
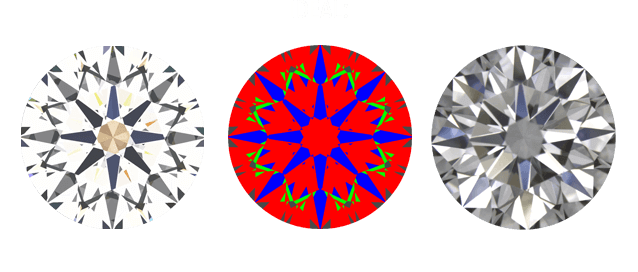

Cut
Cut is the only diamond quality that is controlled by man and can affect the cost of a diamond up to 50%. Therefore, making it the most important of the Four C’s. A poorly cut diamond will be on the low end of the price range and will also not be as beautiful or sparkle as much as a diamond cut to ideal proportions. This is something you have to see in person by comparing them side by side, because there are no two diamonds alike, even though their grades might be exactly the same. Diamond cutters will be paid significantly more for a 1.00ct. diamond than a diamond, let’s say that is .98ct. Many of them will use cutting techniques in order to make these “magic numbers”, by displacing the weight of the diamond to other areas. This means, you are getting a diamond that isn’t cut as well and will not be as beautiful. An ideal cut American Gem Society (AGS) 1.00ct. round brilliant diamond should measure 6.5mm in diameter.
To delve even deeper into cut grading, we should mention Light Performance. Through the Angular Spectrum Evaluation Tool (ASET) and non-contact optical scanning technology we can now measure how well a diamond performs. Or in layman’s terms, how sparkly a diamond is. The better a diamond is cut, the more it will shine, the bigger and more beautiful it will look. Underwood’s is the only company in Jacksonville who buys diamonds with an ASET device, showing the diamond buyers immediately how well the diamond will perform.
Think of a diamond like a window or a prism. The light should go in, reflect to other facets of the diamond and then return back out through the top. In the ASET image you want to see mostly the color red which is light being reflected, some blue color which shows contrast (because you cannot have refraction without contrast or it would look like a head light!) and a little bit of the color green which shows the light reflected at a different angle. This image should look proportional, similar to a snowflake. When you see the colors white, grey or black, that means the light is leaking and the diamond was not cut proportionally. Simply said, the diamond won’t sparkle as much!
Once the diamond is in our AGS accredited gem lab in Jacksonville, FL we put it on a non-contact optical scanner which measures the nine factors which can compromise light performance and calculates a light performance grade automatically (zero being the best and 10 being the worst). We then decide whether we want to keep or reject the diamond. Underwood’s diamond buyers reject an average of 95 out of 100 diamonds.
We are the only store in Jacksonville to use this technology and one of the very few in the entire United States. We encourage you to bring your own diamonds into our stores in Jacksonville and Ponte Vedra Beach, FL to look at them under our ASET devices!
CUT SCALE
AGS Cut
0
GIA IDEAL
1
GIA EXCELLENT
2
GIA VERY GOOD
3
4
GIA GOOD
5
6
7
GIA GOOD
8
9
10
GIA POOR
To learn more about diamonds and cut, watch our video on Underwood’s Diamonds.
COLOR
Natural diamonds come in many different hues and colors. For typical diamond color grading, the scale ranges from colorless (the rarest) to light yellow or light brown. Diamonds come in other colors such as blue, pink, red and green, but are graded as “fancy” colored diamonds and have a separate grading scale.
Underwood’s grades color by using a master set of diamonds which have been previously graded by a reputable gem lab. The diamond grader must be skilled and experienced to select the correct grade according to the saturation and hue.
After the color scale ends at Z (or 10) the diamonds are considered to be a “fancy-color.” Natural diamonds of different colors such as red, pink, blue and green are also considered to be fancy-colored diamonds. There is actually no such thing as a “canary” or “cognac” colored diamond, but instead are proprietary branded terms of diamond companies.






COLOR SCALE
0.0
0.5
1.0
Colorless
D
E
F
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
Near Colorless
G
H
I
J
3.5
4.0
4.5
Faint
K
L
M
5.0
5.5
6.0
6.5
7.0
Very Light
N
O
P
Q
R
7.5
8.0
8.5
9.0
9.5
10.0
TO
Light
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
Fancy Yellow
Fancy Yellow
Fancy Yellow
Colorless (GIA D-F, AGS 0.0-1.0): These diamonds have no color at all and are the rarest. Therefore, they demand the highest prices. Near Colorless (GIA G-J, AGS 1.5-3.0): These diamonds have very little color and when mounted can seem colorless. Faint Color (GIA K-M, AGS 3.5-4.5): These diamonds show some color and will be priced less on the market. Very Light Color (GIA N-R, AGS 5.0-7.0): These diamonds show color which is easily seen in yellow hues. They will be priced even lower. Light Color (GIA S-Z, AGS 7.5-10): These diamonds have a light yellow to brown tint and will be priced the lowest on the market.
FANCY COLOR SCALE
The general fancy-colored diamond grading scale is as follows:
Fancy Light
Fancy
Fancy Dark
Fancy Intense
Fancy Deep
Fancy Vivid
Fancy grading is very specialized and takes a highly trained gemologist in a reputable lab. Fancy colored diamonds can sometimes, but not always, have more value than a colorless diamond. For example, red and blue diamonds are extremely rare, especially when the color is more saturated.
CLARITY
The definition of clarity according to Merriam-Webster is the quality or state of being clear. Diamonds without any inclusions are extremely rare and demand the highest prices. Most diamond characteristics cannot be seen without magnification. When grading clarity, it is the industry standard to do so with a microscope at 10 power (10x) magnification.
While Underwood’s has a huge selection of loose diamonds and engagement rings, we do not believe in selling anything that will affect the durability of a diamond and therefore only sell diamonds with clarities of SI2 or higher.
You should always buy a diamond with a grading report from a reputable gem lab such as the Gemological Institure of America (GIA). On these reports there may be a plot of your diamond which shows the types of inclusions and their definitions. This provides you with a map that is unique to your diamond and can be used for identification if ever in question.
GROW A DIAMOND
I bet you didn’t know diamonds could grow! At Underwood’s we have a trade-in program called “Grow a Diamond.” This means you can buy a diamond today and then trade it in for the amount you paid for it at any time in the future towards something larger. It can be $1 more or $10,000 more, and you can trade it in tomorrow or in twenty years. This applies to solitaire engagement rings, loose diamonds, the center diamond in most engagement rings, diamond solitaire pendants and diamond stud earrings. We like to think that as you get older, your diamonds should get bigger!
Here’s an example of how it works:
• You purchased a pair of 1.00ct. total weight diamond studs last December for $3000 •
• You now want a pair of 1.50ct. total weight diamond studs which are $5900 •
• We give you credit for $3000, taking the 1.00ct. pair back •
• You owe the difference of $2900 •
There is no time limit to this program. Just think, you can get a bigger diamond each year if you wanted! Start your daughter with a small pair of diamond studs and walk her down the aisle at her wedding with 1.00ct. in each ear!

